Introduction
Cisco ASA ROMMON (Read-Only Memory Monitor) is a firmware program that runs on the Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA) hardware. It is responsible for managing the boot process of the device and performing diagnostic tests. ROMMON is stored at the non-volatile memory, which means that it is not erased when the device is powered off. This allows it to perform its functions even if the ASA's operating system is corrupted or unavailable. Some common uses of ROMMON include:
Preparation
The local flash memory of the firewall has been erased. It is necessary to copy a new software image to the firewall using the ROM monitor. Any client can run a TFTPD software and can be used as a server to copy the software from a client to the device. The topology below shows how the devices are connected to each other using a simple RJ45 ethernet cable.

ROMMON
Launching BootLoader...
Searching / for images to boot.
No images in /
Error 15: File not found
unable to boot an image
Booting from ROMMON
Cisco Systems ROMMON Version (2.1(9)8) #1: Wed Oct 26 17:14:40 PDT 2011
Use BREAK or ESC to interrupt boot.
Use SPACE to begin boot immediately.
Boot interrupted.
Management0/0
Link is DOWN
MAC Address: ####.####.####
Use ? for help.
rommon #0>
?
rommon #1> ?
Variables: Use "sync" to store in NVRAM
ADDRESS= local IP address
CONFIG= config file path/name
GATEWAY= gateway IP address
IMAGE= image file path/name
LINKTIMEOUT= Link UP timeout (seconds)
PKTTIMEOUT= packet timeout (seconds)
PORT= ethernet interface port
RETRY= Packet Retry Count (Ping/T FTP)
SERVER= server IP address
VLAN= enable/disable DOT1Q tagging on the selected port
Commands:
? valid command list
address local IP address
boot boot an image, valid args are:
- "image file spec" and/or
- "cfg="
clear clear interface statistics
confreg set hex configuration register
dev display platform interface devices
erase erase storage media
file application image file path/name
gateway gateway IP address
gdb edit image gdb settings
help valid command list
history display command history
interface ethernet interface port
no clear feature settings
ping send ICMP echo
reboot halt and reboot system
reload halt and reboot system
repeat repeat previous command, valid arguments:
- no arg: repeat last command
- number: index into command history table
- string: most recent 1st arg match in command history table
reset halt and reboot system
server server IP address
set display all variable settings
show display cmd-specific information
sync save variable settings in NVRAM
tftpdnld T FTP download
timeout packet timeout (seconds)
trace toggle packet tracing
unset unset a variable name
rommon #2>
APIPA (Automatic Private IP Addressing) is a feature of Microsoft Windows operating systems that enables a computer to automatically assign itself an IP address when it is unable to obtain one from a DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) server. It assigns itself an IP address in the range of 169.254.0.1 to 169.254.255.254. This address is not routable on the internet and is intended for use in private networks only.
CMD Command Prompt
Microsoft Windows [Version 10.0.22621.1555]
(c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
C:\Users\NBLAB01>ipconfig
ipconfig
Microsoft Windows [Version 10.0.22621.1555]
(c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
C:\Users\NBLAB01>ipconfig
Windows IP Configuration
Ethernet adapter Ethernet 2:
Connection-specific DNS Suffix . :
Link-local IPv6 Address . . . . . : fe80::####
Autoconfiguration IPv4 Address. . : 169.254.72.35
Subnet Mask . . . . . . . . . . . : 255.255.0.0
Default Gateway . . . . . . . . . :
Wireless LAN adapter LAN-Verbindung* 1:
Media State . . . . . . . . . . . : Media disconnected
Connection-specific DNS Suffix . :
Wireless LAN adapter LAN-Verbindung* 2:
Media State . . . . . . . . . . . : Media disconnected
Connection-specific DNS Suffix . :
Wireless LAN adapter WLAN:
Connection-specific DNS Suffix . :
Link-local IPv6 Address . . . . . : fe80::####
IPv4 Address. . . . . . . . . . . : 192.168.1.13
Subnet Mask . . . . . . . . . . . : 255.255.255.0
Default Gateway . . . . . . . . . : 192.168.1.254
Ethernet adapter Ethernet:
Media State . . . . . . . . . . . : Media disconnected
Connection-specific DNS Suffix . : configure-networks.com
Mobile Broadband adapter Mobilfunk:
Media State . . . . . . . . . . . : Media disconnected
Connection-specific DNS Suffix . :
C:\Users\NBLAB01>
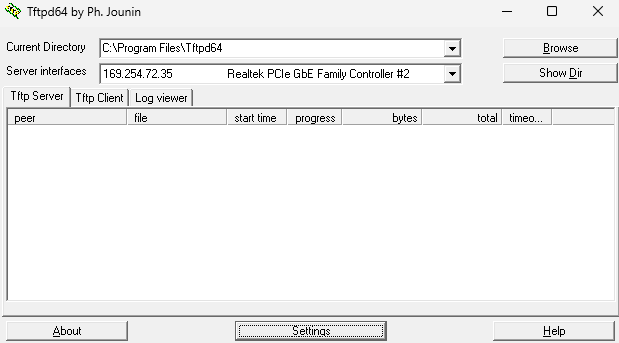
Open TFTPD and choose the interface that has been assigned an IP address by APIPA.
Copy the software images to the TFTPD directory. This is the location from where the firewall will download the software images from.



0 Comments