Introduction
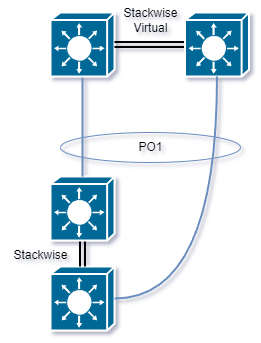
Multichassis Etherchannel is a technology used in networking to create a high-availability connection between two or more switches. It allows multiple physical links to be combined into a single logical link, which enhances the bandwidth and provides redundancy in. In a typical Ethernet channel, all the links belong to a single switch. However, in a Multichassis Etherchannel setup, the links belong to different switches, but they are logically aggregated into a single EtherChannel. This means that the switches are able to work together as a single logical entity, which provides redundancy and high availability. Multichassis Etherchannel works by using a protocol called Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) to establish a logical link between the switches. Each switch participating in the MEC shares information about its physical links with the other switches using LACP, and they negotiate the parameters of the EtherChannel. This includes the number of links, bandwidth, and other configuration options. The benefits of Multichassis Etherchannel include increased bandwidth and fault tolerance. With Multichassis Etherchannel, if a link or switch fails, traffic is automatically redirected to the remaining links, allowing for uninterrupted network connectivity. Additionally, Multichassis Etherchannel provides load balancing across the available links, ensuring that traffic is spread evenly across the network.

0 Comments