Introduction
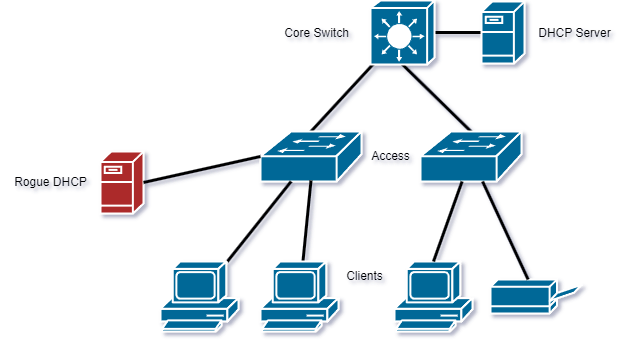
DHCP Snooping is a Cisco security feature that prevents unauthorized or rogue DHCP servers from being deployed on a network. DHCP Snooping works by intercepting all DHCP messages in the network and verifying that they come from a trusted DHCP server. Any DHCP message that does not meet the requirements is dropped. In addition, DHCP Snooping also prevents DHCP spoofing attacks, where an attacker sends a forged DHCP message to the network, with the intention of stealing information or causing network disruption.
Description
DHCP Snooping prevents other DHCP servers from being deployed on a network
DHCP Snooping inspects DHCP messages
It ensures that DHCP messages come from a trusted DHCP server
DHCP Snooping only forwards DHCPDISCOVER broadcast messages from clients to trusted ports
It is a layer 2 security feature, which means that it operates at the data-link layer of the OSI model
DHCP Snooping can prevent several types of DHCP-related attacks, including DHCP spoofing, man-in-the-middle attacks, and denial-of-service attacks
DHCP Snooping is supported on a wide range of Cisco switches, including Catalyst, Nexus, and Meraki switches
DHCP Snooping is not enabled by default on Cisco switches, and it needs to be manually configured
It acts like a firewall between untrusted hosts and trusted DHCP servers
DHCP snooping is enabled on a per-VLAN basis - by default, it is inactive on all VLANs
The default state of all interfaces is untrusted - trusted interfaces need to be configured as such manually

0 Comments