Introduction
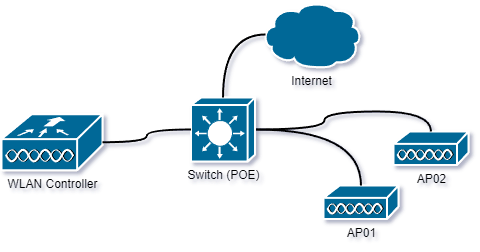
Cisco Lightweight Access Points (LWAPs) are a type of wireless access point used in Cisco's wireless networking solutions. They are designed to work in conjunction with a Cisco Wireless LAN Controller (WLC) to provide centralized control and management of wireless networks.
Description
LWAPs are wireless access points that are "lightweight" in the sense that they do not have the full intelligence or configuration settings built into them.
Instead, they rely on a centralized controller, the Cisco WLC, for configuration, management, and control functions.
LWAPs primarily focus on transmitting and receiving wireless signals, while most of the decision-making and security features are handled by the WLC.
The Cisco WLC is a central device that manages and controls multiple LWAPs within a wireless network.
It provides features such as radio frequency (RF) management, security policies, guest access controls, and roaming support.
The WLC centralizes the configuration and monitoring of the entire wireless network, making it easier to manage and maintain.
Centralized Management: LWAPs offload the configuration and management tasks to the WLC, simplifying network administration.
Seamless Roaming: Cisco LWAPs and WLCs enable seamless mobility for wireless clients as they move within the coverage area, ensuring uninterrupted connectivity.
WLCs provide advanced security features like intrusion detection and prevention, rogue AP detection, and encryption to protect the wireless network.
Load Balancing: WLCs can distribute client connections among LWAPs to ensure even distribution of network traffic and optimal performance.
Quality of Service (QoS): WLCs can prioritize traffic to ensure critical applications receive the necessary bandwidth and quality.
Cisco LWAPs and WLCs are commonly used in enterprise environments where large-scale wireless networks are needed.
They are suitable for industries such as education, healthcare, retail, and hospitality, where reliable and secure wireless connectivity is essential.
Cisco also offers options for both indoor and outdoor LWAPs to cover various deployment scenarios.
Cisco also manufactures Autonomous Access Points (AAPs), which are standalone access points with their own configuration and management interfaces.
LWAPs are generally preferred in larger deployments or environments requiring centralized management, while AAPs are suitable for smaller deployments or those not needing centralized control.

0 Comments