Introduction
A Cisco WLAN Controller is a hardware device or virtual appliance that manages the deployment and configuration of wireless access points (APs) in a Cisco wireless LAN (WLAN) network. The WLAN Controller provides central management of wireless network functions, including security, quality of service (QoS), mobility, and network access control. This centralization simplifies network administration and helps ensure consistent security and performance policies across multiple APs.
Local Mode & FlexConnect
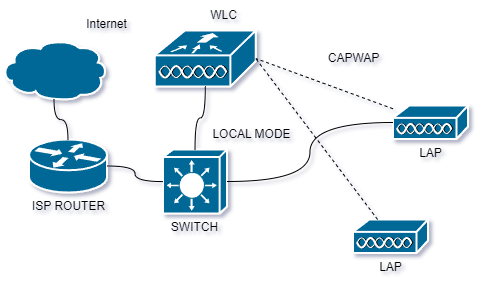
Local Mode is a deployment approach where access points (APs) act as lightweight devices primarily handling radio functions, while most control and management functions are centralized in a Wireless LAN Controller (WLC). In this mode, user data traffic is sent from APs to the WLC, which manages quality of service (QoS), VLAN assignments, and other aspects of wireless traffic. Roaming decisions, configuration, monitoring, and troubleshooting are also handled centrally. Local Mode is suitable for environments with sufficient bandwidth between APs and the central WLC, providing a unified and centrally managed wireless infrastructure. Local Mode ist mostly used in LAN enviromnets where the WLC and the APs belong to the same local network of an organization.
FlexConnect is a feature in Cisco wireless LAN (WLAN) networks that allows for decentralized network management of wireless access points (APs) while still providing centralized control and management capabilities. This allows APs to operate in a standalone mode, with local authentication and data forwarding, while still being centrally managed and configured. In FlexConnect mode, APs can maintain a local copy of the network configuration and security policies, allowing for faster data forwarding and reduced network latency. This can be particularly beneficial in situations where the WLAN network is spread out over a large geographic area, or where network connectivity is unreliable. FlexConnect also supports local switching of data, allowing for traffic to be processed locally at the AP, rather than being sent back to a central controller for processing. This can help reduce network congestion and improve overall network performance.
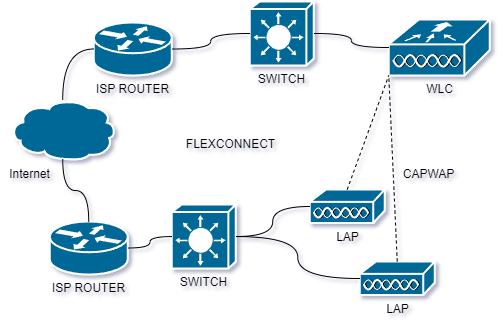
Local mode and FlexConnect mode are two deployment options for Cisco wireless access points (APs) within a Wireless LAN Controller (WLC) environment. These modes determine how traffic is managed and processed, especially in scenarios where the APs need to handle user data and control plane functions differently.
CAPWAP
CAPWAP (Control and Provisioning of Wireless Access Points) is a protocol that is used to manage and control wireless access points (APs) in a wireless LAN (WLAN) network. It provides a standard way for wireless controllers to communicate with APs and manage the configuration and deployment of wireless network resources. CAPWAP allows for the centralization of network management and configuration, which can simplify network administration and improve network security. In a CAPWAP network, the wireless controller acts as the central management point for the wireless network, while APs are responsible for providing wireless coverage and forwarding data between wireless clients and the wired network. The wireless controller and APs communicate using CAPWAP to exchange information and control messages, allowing for centralized management of wireless network functions such as security, quality of service (QoS), mobility, and network access control. CAPWAP is an industry standard and is supported by multiple vendors, allowing for interoperability between different types of wireless network devices. This makes it a popular choice for wireless network deployments in enterprise, service provider, and government environments.
Mobility Groups
Cisco Mobility Groups are a feature in Cisco wireless LAN (WLAN) networks that allow for the central management of multiple wireless controllers and access points (APs). This allows for the creation of a single, unified wireless network, even when the network is spread out over multiple physical locations. In a Cisco Mobility Group, all wireless controllers are aware of each other and can exchange information, allowing for centralized management of wireless network functions such as security, quality of service (QoS), mobility, and network access control. This can simplify network administration and improve network security. When a wireless client roams from one AP to another, the APs communicate with each other through the Mobility Group to ensure a seamless transition of the client’s connection. The Mobility Group also provides centralized mobility management, allowing for the management of wireless clients across multiple physical locations from a single point. Cisco Mobility Groups can also be used to provide redundancy and failover protection, ensuring that if one wireless controller fails, another controller can take over and maintain wireless network operations. This helps ensure high availability and reliability of the wireless network. In summary, Cisco Mobility Groups provide a centralized and scalable solution for wireless network management, allowing for the creation of a unified wireless network across multiple physical locations.

0 Comments