Introduction
A Windows DHCP Server is a network server that automatically assigns IP addresses and other network configuration parameters to devices on a network. DHCP stands for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, and its primary role is to manage the dynamic distribution of IP addresses to devices, ensuring efficient use of IP address space and reducing the administrative burden of manually configuring each device.
Description
IP Address Allocation: The DHCP server assigns IP addresses to clients from a predefined range (scope) when they join the network. This ensures that each device has a unique IP address, preventing conflicts.
Configuration Parameters: In addition to IP addresses, the DHCP server can provide other configuration settings such as subnet masks, default gateways, DNS server addresses, and more. This enables clients to be fully configured for network communication upon receiving an IP address.
Lease Management: The DHCP server assigns IP addresses on a lease basis. This means that each IP address is assigned for a specific period. When the lease expires, the client must request a renewal. This mechanism ensures efficient IP address usage and allows the server to reclaim and reassign IP addresses no longer in use.
Automatic Reconfiguration: If network settings change (such as the DNS server or default gateway), the DHCP server can automatically update all clients with the new configuration without needing manual intervention on each device.
Centralized Management: Simplifies the administration of IP addresses and network settings from a single point.
Efficiency: Automates the IP address assignment process, reducing errors and saving time.
Flexibility: Easily accommodates changes in network configuration and scaling of the network.
Consistency: Ensures that all devices receive consistent network settings, improving overall network reliability and performance.
DORA
DORA stands for the four key steps in the DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) lease process: Discovery, Offer, Request, and Acknowledgment. These steps describe the interaction between a DHCP client and server to obtain an IP address and other network configuration information.
Description
DHCP Discovery: When a device (DHCP client) connects to the network, it sends a DHCPDISCOVER broadcast message to find available DHCP servers.
DHCP Offer: The DHCP server responds with a DHCPOFFER message, which includes an available IP address and other network configuration settings.
DHCP Request: The client responds with a DHCPREQUEST message, indicating acceptance of the offered IP address.
DHCP Acknowledgment: The DHCP server confirms with a DHCPACK message, finalizing the IP address assignment and providing any additional configuration details.
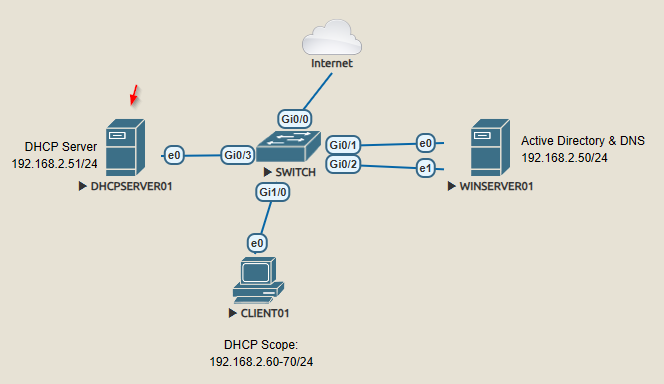
Topology
The following topology will be used for this guide.

0 Comments